The excellent performance of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) and the specific adsorption of target objects make it widely used in artificial antibody simulation, catalysis, drug release, solid phase extraction, chromatography, sensors, and adsorption determination. The main active compound of the Chinese medicine Jiji is Chinonol. Due to the poor selectivity of traditional separation materials, the process of directly extracting cinnonyl alcohol from traditional Chinese medicine is cumbersome and inefficient. A team of pharmaceutical chemistries led by Prof. Yan Ping, a researcher from the Key Laboratory of Northwestern Plant Resources Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences synthesized a new molecularly imprinted polymer by non-covalent imprinting and established a solid phase extraction method. It has been successfully applied to the extraction of diterpenoid chinonol in the extract of Chinese herbal medicine Anoplophora. The molecularly imprinted polymer prepared has good selectivity and adsorption performance for the target analyte, and the recovery rate can reach 80.9%. This method is an effective method for selective extraction and cleaning of plant active ingredients, and can be directly applied to the extraction of cinnonyl alcohol in the complex system of Chinese herbal medicine. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The results of the study were published in the recently published Talanta (89 (2012) 505–512). Talanta published abstract WEIHAI WEFISH OUTDOOR PRODUCTS CO.,LTD , https://www.wefishtackle.com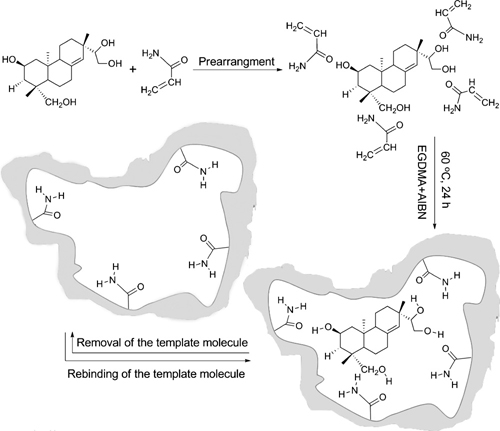 Schematic characterization of chinonol-molecularly imprinted polymer
Schematic characterization of chinonol-molecularly imprinted polymer