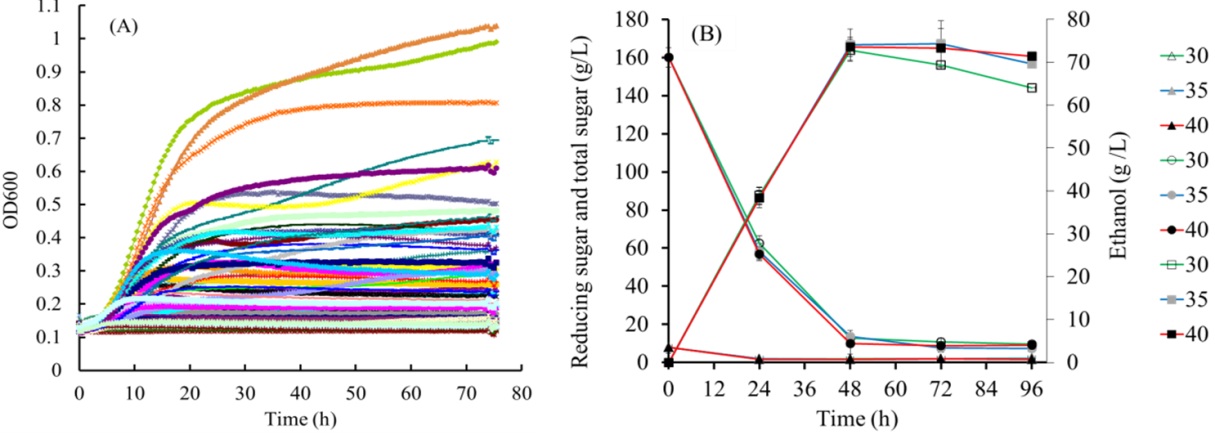
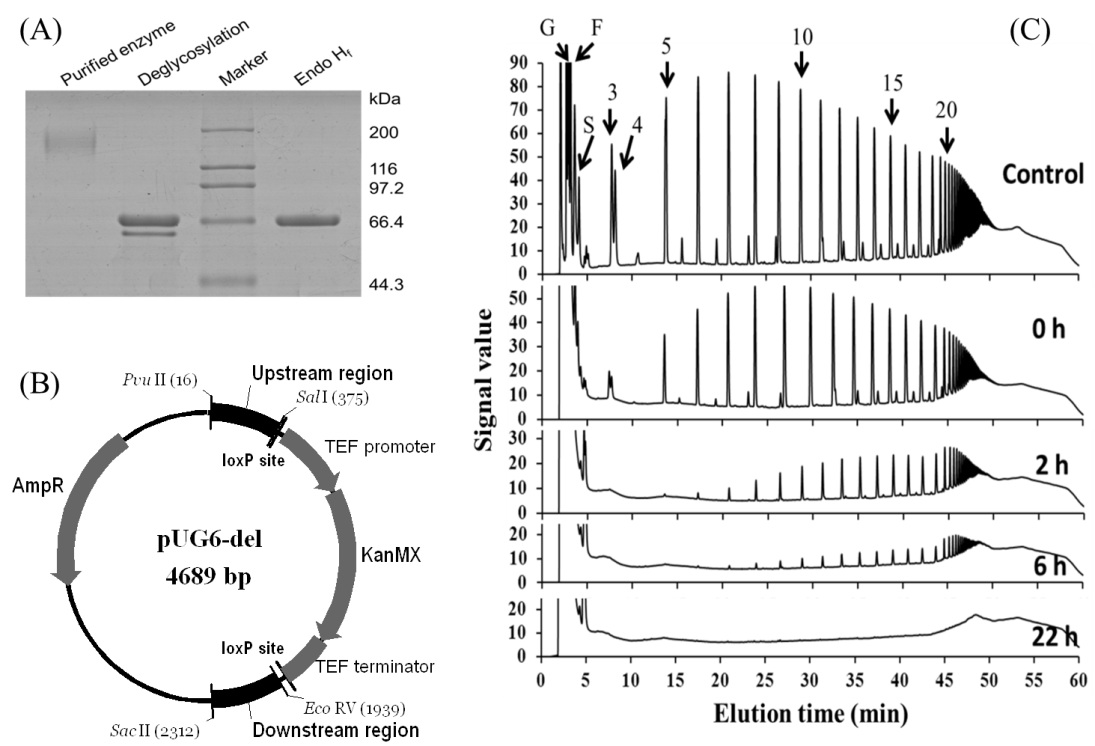
Recently, Researcher Li Welfare and Dr. Shian Wang of the Microbial Resources Team of the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Processes, Chinese Academy of Sciences have made a series of phased progress in the research of ethanol bio-processing of S. cerevisiae Jerusalem artichoke. Jerusalem artichoke, also known as Jerusalem artichoke, is a new type of energy plant. It has strong soil adaptability, no pests and diseases, and can be planted on non-cultivated marginal land such as drought and salt. The production of ethanol from Jerusalem artichoke or Jerusalem artichoke industrial waste residue is one of the important directions for the development of fuel ethanol. The main polysaccharide component that can be converted into ethanol in Jerusalem artichoke is inulin. The integrated bioprocessing process integrates inulinase production, inulin hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation into the same process, which can directly ferment Jerusalem artichoke to produce fuel ethanol. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the best strain for large-scale production of ethanol, but the strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae found in the past do not have the ability to hydrolyze inulin. Li Fuli et al. Obtained a strain of S. cerevisiae with temperature tolerance inulin metabolism through yeast resource screening and stress resistance evaluation. This strain fermented 200 g / L Jerusalem artichoke powder at 40 ºC and produced 65.2 g / L ethanol The ethanol yield is 79.7%, which is the highest reported yield and yield of ethanol fermentation of non-engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae Jerusalem artichoke. The traditional ethanol fermentation temperature is 30 ºC to 35 ºC, and increasing the fermentation temperature by 5 ºC can significantly reduce the cost. The ability to ferment normally at 40 ºC reflects the advantages of this strain. The related research results were published in Appl Microbiol Biotechnol (2012) 95: 1359–1368, and obtained one Chinese invention authorization patent (ZL201010111324.4). The discovery of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with inulin metabolism broke through the idea that S. cerevisiae cannot metabolize inulin. So, which enzyme in Saccharomyces cerevisiae catalyzes the hydrolysis of inulin? Using molecular biology and genetics methods, Li Fuli et al. Revealed that the key enzyme responsible for the hydrolysis of inulin in S. cerevisiae is an exoinvertase SUC2, which belongs to the international Saccharomyces cerevisiae inulin hydrolase was first discovered on the site. Related research results were published online in Appl Environ Microbiol (DOI: 10.1128 / AEM.02658-12). In the screening of inulin metabolism yeast resources, a new strain of efficient inulin metabolism yeast was also obtained. Through protein purification and gene cloning, the new inulinase and inulinase genes of the strain were revealed. Compared with the most widely used exo-inulinase gene of Kluyveromyces marxianus, the new inulinase gene was expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and the transformants showed higher inulin metabolism. Related research results were published online in Appl Microbiol Biotechnol (DOI 10.1007 / s00253-012-4108-y). The discovery of Saccharomyces cerevisiae inulin hydrolase and new inulinase provides new ideas for further development of Jerusalem artichoke ethanol integrated bioprocessing strains. The high-polymerization inulin molecule is the main limiting factor for inulin fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. If an exogenous endo-inulinase gene is introduced into Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the high-polymerization inulin can be cut into the low-polymerization degree by the action of endozyme Oligosaccharides, these oligosaccharide molecules are easily hydrolyzed by exonuclease, thereby improving the hydrolysis efficiency of inulin and the ethanol fermentation efficiency of Jerusalem artichoke. Based on this assumption, Li Fuli and others are conducting research on the exogenous expression of S. cerevisiae endo-inulinase gene. In order to further improve the activity of S. cerevisiae endo-inulinase gene, new inulinase gene is introduced at the same time. The goal of the next stage is to achieve an ethanol yield of Jerusalem artichoke ethanol fermentation from 79.7% to more than 90% at 40 ºC and Jerusalem artichoke powder greater than 200 g / L, and advance this project to the pilot test stage. Figure 1. Jerusalem artichoke ethanol Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain (A) Screening of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with inulin metabolism; (B) Jerusalem artichoke powder fermentation at different temperatures Figure 2. The discovery of Saccharomyces cerevisiae inulin hydrolase (A) Purification of Saccharomyces cerevisiae inulin hydrolase; (B) Gene knockout vector; (C) Enzymolysis dynamics of inulin hydrolase There are nice quality and price Paddle board .Accessories including everything you need to enjoy your day on the water including: your board, collapsible aluminum paddle, safety leash , hand pump , waterproof bag for essentials such as cell phone and keys, and an upgraded backpack to hold everything. WEIHAI HITEAM TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.paddleboardmanufacturer.com